TL;DR: Artificial Intelligence is transforming Kenya’s healthcare, agriculture, fintech, and education sectors. Kenya ranks 71st globally in AI readiness and has launched a National AI Strategy 2025-2030. Key challenges include data scarcity, skills gaps, and infrastructure limitations, but opportunities for economic growth and innovation are significant. This guide covers AI fundamentals, local applications, learning resources, policies, case studies, and how to get started with AI in Kenya.
- What is Artificial Intelligence and why should Kenyans care about it?
- How does Artificial Intelligence actually work in simple terms?
- How is AI changing healthcare in Kenya?
- What ways is AI helping Kenyan farmers?
- How are Kenyan banks using AI?
- Can AI really improve education in Kenya?
- What is the Kenyan government doing with AI?
- Where can Kenyans learn Artificial Intelligence skills?
- What rules govern AI in Kenya?
- What’s holding back AI in Kenya?
- How can Kenya benefit from AI?
- What are some successful AI examples in Kenya?
- What’s next for AI in Kenya?
- How can I get involved with AI in Kenya?
- For Students and Beginners
- For Professionals and Career Changers
- For Entrepreneurs and Business Owners
- For Policymakers and Government Officials
- Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Kenya
- What’s the current state of AI in Kenya?
- How are Kenyan farmers actually using AI today?
- Can I really learn AI without a technical background?
- Is the Kenyan government using AI to monitor citizens?
- Will AI take away jobs in Kenya?
- How much does it cost to implement AI in a Kenyan business?
- What languages do AI systems in Kenya support?
- How can I protect my data when using AI services in Kenya?
- Conclusion: Joining Kenya’s AI Journey
What is Artificial Intelligence and why should Kenyans care about it?
Artificial Intelligence refers to computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Kenyans should care about AI because it’s solving local problems while creating new economic opportunities across the country.
AI could add approximately $15 billion to Kenya’s economy by 2030, according to government estimates. Kenya ranks 71st globally in the Government AI Readiness Index 2020, leading in East Africa. Over 60% of Kenyan businesses have started exploring or implementing AI solutions in their operations. The Kenyan government has launched a National AI Strategy 2025-2030 to guide the country’s AI development.
AI isn’t just for tech companies, it’s helping farmers detect crop diseases, enabling doctors to diagnose illnesses earlier, allowing banks to serve more customers, and helping students learn more effectively. For a country with Kenya’s challenges and opportunities, AI offers tools to accelerate development and improve lives.
How does Artificial Intelligence actually work in simple terms?
AI works by using computer algorithms to recognize patterns in data, learn from those patterns, and then make predictions or decisions based on what it has learned. Think of it like teaching a child through examples rather than giving them explicit instructions for every situation.
AI systems process massive amounts of data, often millions of examples, to identify patterns. Machine Learning, a subset of AI, allows systems to improve their performance without being explicitly programmed. For example, an AI system learns to identify crop diseases by analyzing thousands of images of both healthy and diseased plants. Once trained, the AI can identify diseases in new images it has never seen before.
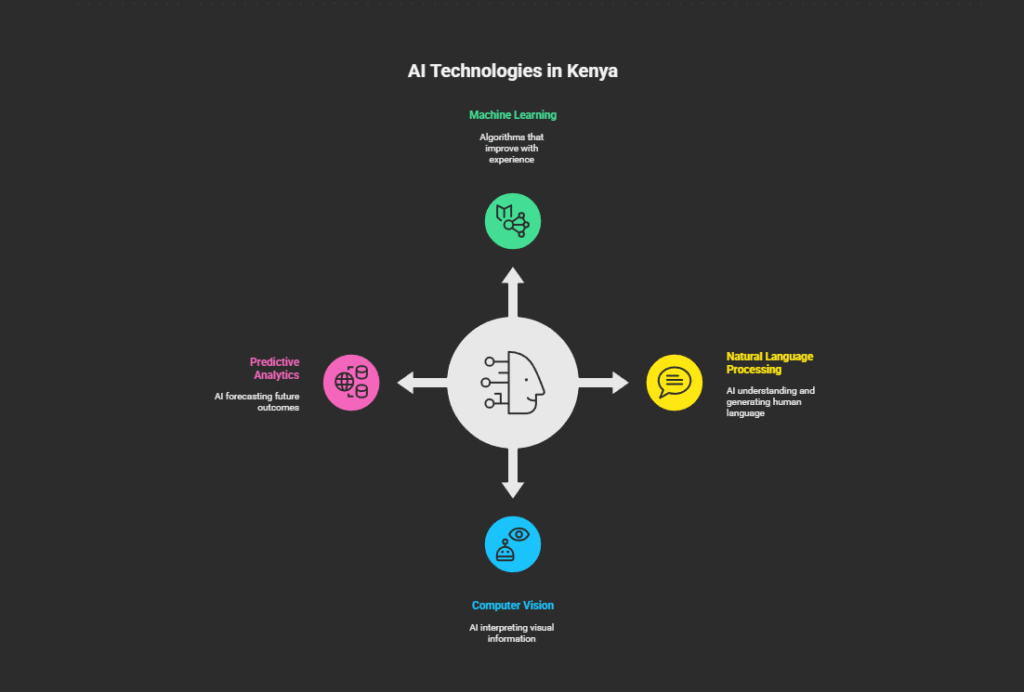
The main types of AI technologies you’ll encounter in Kenya include:
- Machine Learning: Algorithms that get better at tasks through experience
- Example: M-Kopa’s system that learns from mobile money usage to determine creditworthiness
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI that understands and generates human language
- Example: Safaricom’s “Zuri” chatbot that understands customer queries in English and Swahili
- Computer Vision: AI that can interpret and understand visual information
- Example: Apps that identify crop diseases from smartphone photos
- Predictive Analytics: AI that forecasts future outcomes based on historical data
- Example: Systems that predict loan default risk for mobile lenders
How is AI changing healthcare in Kenya?
AI is transforming Kenyan healthcare by improving disease detection, expanding access to medical expertise, and making health systems more efficient. This is particularly important in a country with one doctor for every 16,000 people.
AI diagnostic tools can detect certain diseases up to 30% faster than traditional methods. Telemedicine platforms using AI have expanded specialist access to rural areas by over 40%. The Kenyan Ministry of Health estimates AI could help reduce diagnostic errors by up to 25%. Local health tech startups have collectively served over 500,000 patients.
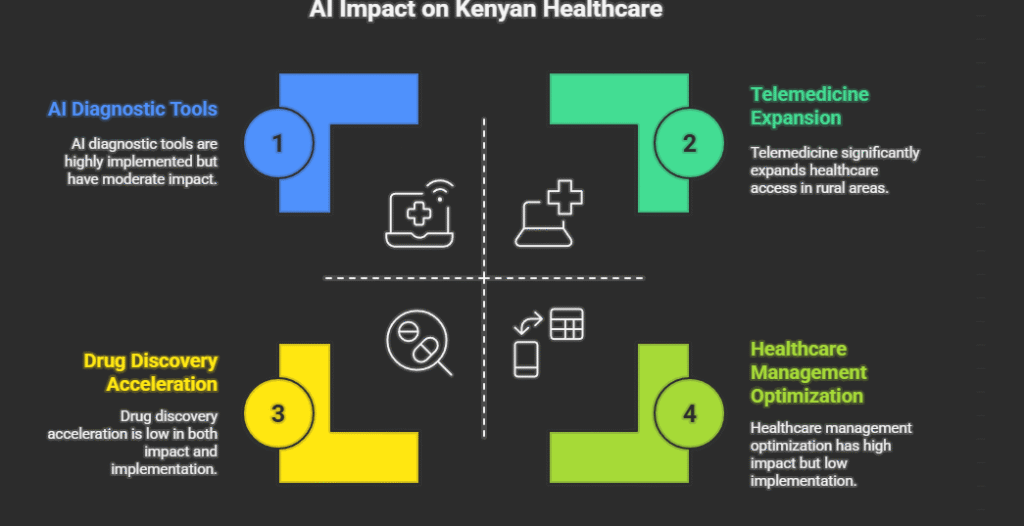
Specific ways AI is changing healthcare in Kenya:
- Disease Detection and Diagnosis
- AI systems analyze medical images to detect conditions like tuberculosis, cervical cancer, and malaria
- For example, AI powered portable ultrasound devices help community health workers identify complications during pregnancy
- Telemedicine and Remote Care
- Platforms use AI chatbots to provide preliminary diagnoses
- These systems help triage patients and determine who needs urgent care versus who can be treated at home
- Drug Discovery and Research
- Researchers at the University of Nairobi use AI to accelerate development of treatments for tropical diseases
- AI analysis can reduce drug discovery time from years to months in some cases
- Healthcare Management
- AI systems help hospitals optimize resource allocation and predict patient admission rates
- During COVID-19, AI models helped Kenya predict outbreak hotspots and allocate resources accordingly
What ways is AI helping Kenyan farmers?
AI is helping Kenyan farmers by providing precise information about crop health, weather patterns, and optimal farming practices. This is especially valuable for the 70% of rural Kenyans who depend on agriculture but face climate change and resource constraints.
Farmers using AI powered agricultural apps have seen yield increases of 20-30% on average. AI crop disease detection can identify problems up to 2 weeks earlier than visual inspection. Platforms like Apollo Agriculture have served over 100,000 Kenyan smallholder farmers. The Kenyan Ministry of Agriculture estimates precision farming could increase agricultural productivity by up to 40% by 2030.
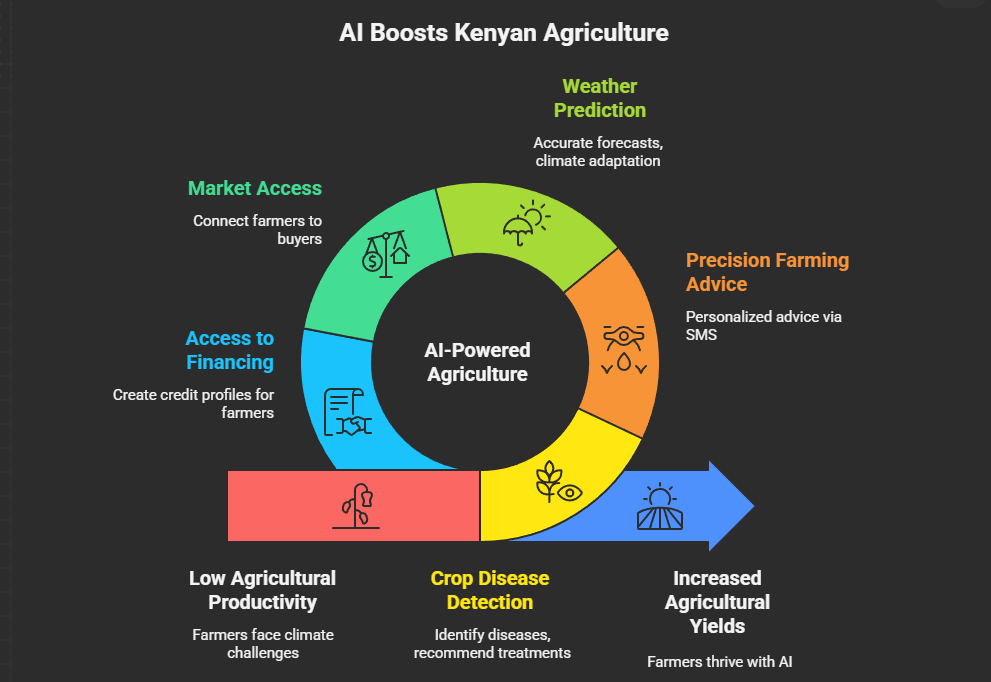
Key AI applications in Kenyan agriculture:
- Crop Disease and Pest Detection
- AI apps use smartphone cameras to identify crop diseases and recommend treatments
- For example, the PlantVillage app has helped over 50,000 farmers identify maize lethal necrosis
- Precision Farming Advice
- AI systems analyze soil data, weather forecasts, and crop characteristics to provide personalized farming advice
- Apollo Agriculture delivers this advice via SMS, making it accessible even without smartphones
- Weather and Climate Prediction
- AI models process weather data to provide accurate forecasts and climate adaptation advice
- These systems help farmers decide when to plant, irrigate, and harvest
- Market Access and Price Information
- Platforms like M-Farm use AI to provide real-time price information and connect farmers directly to buyers
- This helps farmers get better prices and reduces exploitation by middlemen
- Access to Financing
- AI systems analyze farm data and mobile money usage to create credit profiles for farmers
- This enables financial institutions to offer loans to farmers who traditionally lacked access to credit
How are Kenyan banks using AI?
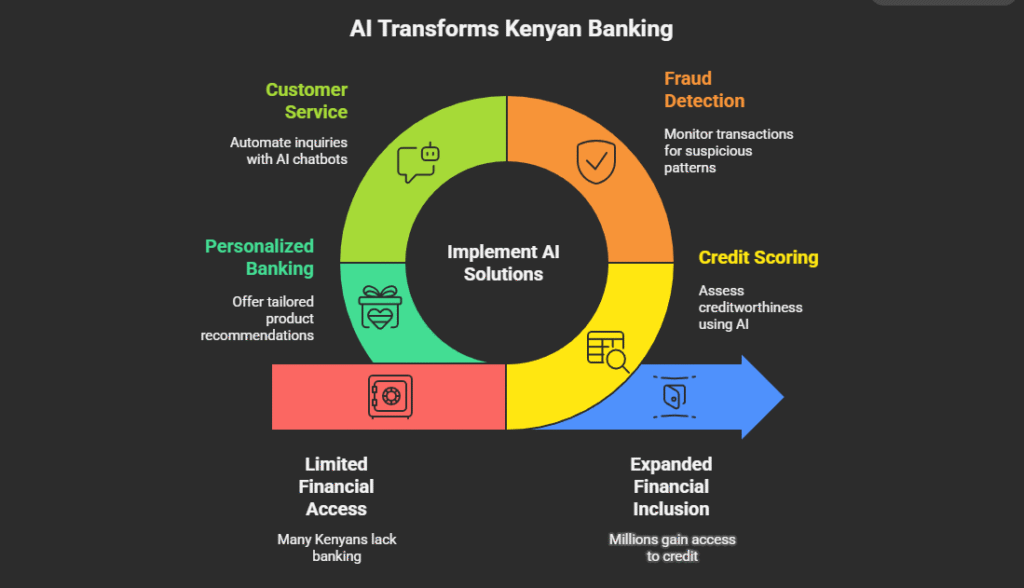
Kenyan banks are using AI primarily to improve customer service, detect fraud, assess credit risk, and personalize financial products. This helps them serve more customers, including the unbanked population that mobile money has brought into the financial system.
AI powered fraud detection systems have reduced banking fraud by approximately 35% in institutions using them. Mobile lenders using AI for credit scoring have provided over $1 billion in loans to Kenyans previously excluded from formal banking. Banks using AI chatbots have reduced customer service costs by up to 30% while improving satisfaction. Equity Bank, one of Kenya’s largest, reports that AI systems help them process loan applications 60% faster.
Specific ways Kenyan financial institutions are using AI:
- Credit Scoring and Lending
- AI algorithms analyze mobile money transactions, utility payments, and other data to assess creditworthiness
- Companies like Branch and Tala use this approach to provide instant loans to millions of Kenyans
- This has expanded financial inclusion, with studies showing AI powered lending has reached over 5 million Kenyans previously without access to credit
- Fraud Detection and Security
- AI systems monitor transactions in real-time to identify suspicious patterns
- These systems can block fraudulent transactions before they are completed, protecting both customers and banks
- For example, Co-operative Bank of Kenya uses AI to analyze millions of transactions daily for signs of fraud
- Customer Service Automation
- AI chatbots handle routine customer inquiries, freeing human agents for more complex issues
- Safaricom’s “Zuri” chatbot resolves over 20 million queries annually
- These systems are increasingly able to communicate in local languages like Swahili and Sheng
- Personalized Banking
- AI analyzes customer behavior to offer personalized product recommendations
- Banks can predict when customers might need specific services, such as loans or insurance
- This personalization has increased product uptake by up to 25% in some institutions
Can AI really improve education in Kenya?
Yes, AI can significantly improve education in Kenya by personalizing learning, automating administrative tasks, and expanding access to quality education. This is particularly important in a country facing teacher shortages, overcrowded classrooms, and unequal access to educational resources.
Students using AI powered personalized learning platforms have shown test score improvements of 20-30%. AI administrative tools have reduced teacher paperwork by up to 40%, allowing more time for instruction. Platforms like Eneza Education have reached over 5 million learners across Kenya. The Kenya Institute of Curriculum Development has identified AI as a key tool for achieving curriculum reform goals.
Ways AI is improving Kenyan education:
- Personalized Learning
- AI systems adapt content to individual student needs, learning pace, and style
- Eneza Education’s platform provides customized quizzes and lessons based on student performance
- This approach helps both struggling students who need extra support and advanced students who can move faster
- Language Support
- AI translation tools help overcome language barriers in education
- Some platforms can translate educational content between English, Swahili, and local languages
- This is particularly valuable in rural areas where students may not be proficient in English
- Administrative Efficiency
- AI systems automate grading, attendance tracking, and report generation
- This reduces the administrative burden on teachers, allowing more time for actual teaching
- For example, some schools using AI for report card generation have reduced the time spent from days to hours
- Expanded Access to Quality Education
- AI powered educational platforms can reach students in remote areas
- These platforms often work on basic mobile phones, not requiring smartphones or computers
- During school closures, such as during COVID-19, these tools helped maintain learning continuity
- Teacher Support and Training
- AI systems provide teachers with insights about student progress and areas needing attention
- Some platforms offer teachers suggestions for improving their instructional methods
- This helps teachers, especially those with limited training, to be more effective
What is the Kenyan government doing with AI?
The Kenyan government is developing policies, implementing AI systems in public services, and creating infrastructure to support AI adoption as part of its digital transformation strategy and Vision 2030 development goals.
The government launched the National AI Strategy 2025-2030 in March 2025. Kenya ranks 71st globally in government AI readiness, the highest in East Africa. The government has allocated KES 5 billion in the current budget for digital transformation initiatives including AI. Over 15 government agencies are currently piloting or implementing AI solutions.
Key government AI initiatives:
- National AI Strategy 2025-2030
- Provides a roadmap for AI development and adoption in Kenya
- Focuses on building infrastructure, developing human capital, creating enabling regulations, and promoting ethical AI
- Aims to position Kenya as Africa’s leader in responsible AI innovation
- AI in Public Service Delivery
- Immigration department uses AI for passport application processing, reducing wait times from weeks to days
- Kenya Revenue Authority employs AI for tax compliance monitoring and fraud detection
- AI systems help optimize public service centers like Huduma Centers
- Smart City Development
- Konza Technopolis is being developed as a smart city with integrated AI systems
- Nairobi County is implementing AI for traffic management, waste collection optimization, and security surveillance
- These systems aim to improve urban efficiency and service delivery
- Healthcare AI Implementation
- Ministry of Health is piloting AI diagnostic tools in public hospitals
- AI systems help with disease surveillance and outbreak prediction
- Telemedicine programs using AI are expanding to rural public health facilities
- Agricultural Support
- Government agricultural extension services are incorporating AI tools
- AI powered systems provide farmers with weather information and market prices
- These initiatives support the government’s food security agenda
Where can Kenyans learn Artificial Intelligence skills?
Kenyans can learn AI skills through universities, online platforms, coding bootcamps, and tech communities. Options range from free introductory courses to specialized degree programs, making AI education increasingly accessible across the country.
Over 20 Kenyan universities now offer AI related courses or programs. Free online AI courses have enrolled over 50,000 Kenyan learners in the past two years. Coding bootcamps report a 90% employment rate for their AI program graduates. The government has set a goal to train 10,000 AI specialists by 2030 through various initiatives.
Best places to learn AI in Kenya:
- University Programs
- University of Nairobi offers AI courses within their computer science and engineering programs
- Strathmore University has a dedicated AI research lab and industry partnerships
- Kenyatta University includes AI modules in their IT and data science programs
- Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology focuses on AI applications in agriculture and engineering
- Online Learning Platforms
- Kenya.ai offers a free Beginner Track specifically designed for Kenyans
- Elements of AI by the University of Helsinki is free and available globally
- Coursera partners with institutions like deeplearning.ai offering courses accessible in Kenya
- IBM SkillsBuild provides free AI courses with certification options
- Coding Bootcamps and Training Programs
- Moringa School offers intensive data science and AI programs with job placement support
- eMobilis provides mobile technology and AI training with scholarship opportunities
- Andela includes AI components in its software development training
- Africa’s Talking offers developer training including AI integration
- Communities and Networking
- AI Kenya community hosts regular meetups, workshops, and hackathons
- iHub Nairobi serves as a tech hub hosting AI events and incubation
- Nairobi Dev School has AI focus groups and learning circles
- Women in AI Kenya promotes gender diversity in the field through mentorship and training
What rules govern AI in Kenya?
Kenya currently doesn’t have specific AI legislation, but AI systems are governed by existing laws like the Data Protection Act (2019). The government is developing more comprehensive regulations through the National AI Strategy 2025-2030 and other policy initiatives.
The Data Protection Act (2019) is the primary legislation affecting AI systems, particularly regarding data privacy. The National AI Strategy 2025-2030 includes recommendations for AI governance and regulation. Kenya has established a Blockchain and AI Taskforce to guide policy development. The Communications Authority of Kenya has published guidelines on AI ethics in telecommunications.
Current regulatory framework for AI in Kenya:
- Data Protection and Privacy
- The Data Protection Act (2019) governs how AI systems collect, process, and store personal data
- It requires consent for data collection and gives individuals rights over their data
- The Office of the Data Protection Commissioner enforces these regulations
- Sector-Specific Guidelines
- Central Bank of Kenya has issued guidelines for AI use in financial services
- Communications Authority of Kenya regulates AI applications in telecommunications
- Ministry of Health has ethical guidelines for AI in healthcare
- Consumer Protection
- The Consumer Protection Act applies to AI products and services
- It requires transparency and fair practices, including in automated decision-making
- Competition Authority of Kenya monitors AI for potential anti-competitive behavior
- Intellectual Property
- Copyright and patent laws apply to AI creations and inventions
- Kenya Intellectual Property Office is developing specific guidelines for AI generated content
- Future Regulatory Developments
- The National AI Strategy 2025-2030 calls for developing comprehensive AI legislation
- Proposed regulations include algorithmic transparency requirements and impact assessments
- The government is considering establishing an AI regulatory authority
What’s holding back AI in Kenya?
AI adoption in Kenya faces several significant challenges including limited data availability, infrastructure gaps, shortage of skilled professionals, funding constraints, and ethical concerns. All of these are slowing the potential benefits of AI technologies across the country.
Only 35% of rural Kenya has reliable internet connectivity, limiting AI access. Kenya has fewer than 1,000 specialized AI professionals despite growing demand. AI startups in Kenya raised only $50 million in 2023, compared to $1.5 billion in South Africa. A 2023 survey found that 68% of Kenyan businesses cite data quality as a major barrier to AI adoption.
Key challenges facing AI in Kenya:
- Data Scarcity and Quality
- Limited availability of high-quality, locally relevant data for training AI systems
- Data silos prevent sharing between government agencies and private companies
- Concerns about data privacy limit collection and use of information
- Only about 40% of Kenyan organizations have mature data management practices
- Infrastructure Limitations
- Inconsistent internet connectivity, especially in rural areas (35% rural penetration)
- Unreliable electricity supply affects operations of AI systems
- Limited cloud computing infrastructure increases costs for AI developers
- High costs of devices and equipment needed for AI applications
- Skills Gap
- Shortage of specialized AI talent, with only a few hundred experts in the country
- Limited AI content in school and university curricula
- Brain drain as skilled professionals seek opportunities abroad
- Need for continuous learning as AI technologies evolve rapidly
- Funding and Investment Constraints
- Limited venture capital for deep-tech AI startups
- High development costs for AI solutions
- Unclear return on investment deters businesses from AI adoption
- Government funding for AI research and development remains limited
- Ethical and Social Concerns
- Risk of AI systems perpetuating existing social biases
- Privacy concerns around data collection and use
- Potential job displacement in certain sectors
- Lack of public understanding and trust in AI systems
How can Kenya benefit from AI?
Kenya can benefit from AI through economic growth, improved public services, increased productivity in key sectors, job creation in new fields, and solutions to local challenges. There is potential to add billions to the economy and significantly improve quality of life across the country.
AI could contribute up to $15 billion to Kenya’s GDP by 2030, according to government estimates. AI powered agricultural solutions could increase food production by up to 40%. The National AI Strategy projects AI could create over 100,000 new jobs by 2030. Early adopters of AI in Kenyan businesses report productivity improvements of 25-35%.
Key opportunities for Kenya through AI:
- Economic Growth and Competitiveness
- AI can boost productivity across sectors, contributing significantly to GDP growth
- Kenya can position itself as Africa’s AI hub, attracting investment and talent
- AI driven innovation can create new industries and business models
- Improved efficiency can make Kenyan businesses more competitive globally
- Solving Local Challenges
- AI can address uniquely African problems with tailored solutions
- Applications in agriculture can improve food security and farmer incomes
- Healthcare AI can extend specialist capabilities to underserved areas
- AI systems can help optimize resource use in energy, water, and other critical areas
- Job Creation and Transformation
- While some jobs may be automated, new roles will emerge in AI development, ethics, and maintenance
- AI can create opportunities for digital work that can be done from anywhere
- New businesses and services will develop around AI technologies
- The government estimates AI could create over 100,000 direct and indirect jobs by 2030
- Improved Public Services
- AI can make government services more efficient and accessible
- Smart city applications can improve urban living conditions
- AI can help optimize resource allocation in education, healthcare, and social services
- Predictive analytics can improve planning and policy-making
- International Collaboration and Leadership
- Kenya can lead in developing AI solutions relevant to developing economies
- Partnerships with global tech companies can bring investment and expertise
- Kenya can influence international AI governance discussions
- Opportunity to become a model for ethical AI adoption in Africa
What are some successful AI examples in Kenya?
Kenya has numerous successful AI implementations across sectors, including M-Kopa’s AI powered financing for off-grid assets, Apollo Agriculture’s precision farming platform, Twiga Foods’ supply chain optimization, Safaricom’s customer service AI, and iProcure’s agricultural marketplace. These demonstrate AI’s practical impact on everyday challenges.
These five case studies collectively serve over 7 million Kenyans. They have raised more than $300 million in combined investment. They demonstrate revenue growth of 40-120% after implementing AI solutions. They’ve created over 5,000 direct jobs and many more indirect opportunities.
Notable AI success stories in Kenya:
- M-Kopa: AI Powered Asset Financing
- Problem: Low-income households unable to access financing for essential assets
- AI Solution: Machine learning algorithms analyze mobile money data to create credit scores
- Impact: Over 3 million customers financed for solar systems, smartphones, and other assets
- Lesson: Alternative data can effectively serve the unbanked population
- Apollo Agriculture: Precision Farming for Smallholders
- Problem: Smallholder farmers struggling with low productivity and climate change
- AI Solution: Satellite imagery and AI provide customized farming advice and financing
- Impact: 100,000+ farmers served with 30% average yield increase
- Lesson: AI can democratize access to agricultural expertise
- Twiga Foods: Supply Chain Optimization
- Problem: Inefficient food supply chain with high waste and price volatility
- AI Solution: Predictive analytics optimize inventory and logistics
- Impact: Reduced food waste by 25%, stabilized prices for vendors
- Lesson: AI can transform traditional value chains for greater efficiency
- Safaricom’s Customer Service AI
- Problem: High volume of customer inquiries overwhelming call centers
- AI Solution: NLP powered chatbot “Zuri” handles routine inquiries
- Impact: 20 million+ queries resolved annually, reduced wait times
- Lesson: AI can scale customer service while maintaining quality
- iProcure: Agricultural Supply Chain AI
- Problem: Farmers lacking access to quality inputs and fair markets
- AI Solution: Platform connects farmers to suppliers and buyers using predictive analytics
- Impact: 50,000+ farmers served, increased income by 15-20%
- Lesson: AI can create transparent marketplaces that benefit all participants
What’s next for AI in Kenya?
The future of AI in Kenya includes widespread adoption across sectors, job transformation, improved public services, agricultural revolution through precision farming, and healthcare access expansion. This positions Kenya as a potential leader in AI innovation for Africa while addressing uniquely local challenges.
The National AI Strategy 2025-2030 projects AI will be standard in most sectors by 2030. Government forecasts AI could create 100,000+ new jobs while transforming existing ones. Investment in Kenyan AI startups has grown at 65% annually over the past three years. Kenya ranks among the top 3 African countries in AI readiness and innovation.
Key developments to expect in Kenya’s AI future:
- Widespread Sector Adoption (2025-2030)
- AI will become standard in banking, agriculture, healthcare, and government services
- Medium and small businesses will increasingly adopt AI tools
- AI integration will expand from Nairobi and major cities to secondary towns and rural areas
- By 2030, over 50% of Kenyan businesses are expected to use AI in some capacity
- Job Market Transformation
- While some routine jobs will be automated, new roles will emerge in AI development, ethics, and maintenance
- Demand for AI skills will grow across sectors, not just in tech companies
- There will be increased emphasis on reskilling and upskilling programs
- New education pathways focused on AI and related technologies will emerge
- Improved Public Services
- AI will enhance efficiency in tax collection, service delivery, and resource allocation
- Smart city initiatives will expand beyond Nairobi to other urban centers
- AI powered systems will help reduce corruption and improve transparency
- Government services will become more personalized and accessible through AI interfaces
- Agricultural Revolution
- AI driven precision farming will significantly boost productivity and climate resilience
- Smallholder farmers will increasingly access AI tools through mobile platforms
- AI will help optimize water use, reduce waste, and improve market access
- Agricultural AI could help Kenya achieve food security and become a food exporter
- Healthcare Transformation
- AI diagnostics will extend specialist capabilities to remote areas
- Predictive health systems will shift focus from treatment to prevention
- AI will help manage disease outbreaks and optimize resource allocation
- Telemedicine with AI components will become standard in the healthcare system
How can I get involved with AI in Kenya?
You can get involved with AI in Kenya by learning basic skills through free online courses, joining tech communities, starting with small projects, pursuing formal education or training, and participating in AI events and competitions. This applies whether you’re a student, professional, entrepreneur, or policymaker.
Free AI courses have enrolled over 50,000 Kenyans in the past two years. AI Kenya community has grown to over 10,000 members across the country. Kenyan AI startups raised over $50 million in 2023, creating new job opportunities. Universities report 300% increase in enrollment for AI related courses over the past three years.
Specific ways to get started with AI in Kenya:
For Students and Beginners
- Start with Free Online Resources
- Take the Kenya.ai Beginner Track for locally relevant content
- Complete the Elements of AI course for fundamental concepts
- Explore Google’s Machine Learning Crash Course for technical foundations
- Join IBM SkillsBuild for free certification courses
- Join Communities and Networks
- Attend AI Kenya meetups and workshops in your area
- Participate in online forums and social media groups focused on AI
- Connect with mentors who can guide your learning journey
- Find study groups to collaborate on projects and share knowledge
- Build Practical Skills Through Projects
- Start with simple projects using public datasets
- Participate in hackathons and AI competitions
- Contribute to open-source AI projects
- Create a portfolio of your work to showcase your skills
For Professionals and Career Changers
- Upskill Through Targeted Training
- Enroll in specialized AI programs at Moringa School or eMobilis
- Take online courses in specific AI technologies relevant to your field
- Pursue certifications in high-demand areas like machine learning or data science
- Attend workshops and conferences to stay updated on latest developments
- Apply AI in Your Current Role
- Identify processes in your work that could benefit from AI
- Propose and lead AI pilot projects in your organization
- Collaborate with technical teams to implement AI solutions
- Document and share your experiences and results
For Entrepreneurs and Business Owners
- Identify AI Opportunities
- Look for problems in your industry that AI could solve
- Research how similar businesses globally are using AI
- Assess your data assets and how they could fuel AI applications
- Consider partnerships with AI technology providers
- Start Small and Scale
- Begin with pilot projects to demonstrate value
- Measure ROI carefully before expanding AI initiatives
- Invest in data infrastructure as a foundation for AI
- Build or hire AI expertise as your needs grow
For Policymakers and Government Officials
- Support the National AI Strategy
- Align your department’s initiatives with the national strategy
- Advocate for resources to implement AI programs
- Develop policies that balance innovation with protection
- Create regulatory sandboxes for testing AI innovations
- Promote AI Education and Awareness
- Include AI in school curricula and technical training programs
- Support public awareness campaigns about AI benefits and risks
- Fund research and development in AI applications
- Facilitate international collaboration and knowledge sharing
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Kenya
What’s the current state of AI in Kenya?
Kenya has emerging AI adoption in key sectors like fintech, agriculture, and healthcare. The country ranks 71st globally in AI readiness and has launched a National AI Strategy 2025-2030. While challenges remain, the ecosystem is growing rapidly with increasing investment and talent development.
How are Kenyan farmers actually using AI today?
Kenyan farmers are using AI through smartphone apps that identify crop diseases, SMS based systems that provide farming advice, platforms that connect them to markets and financing, and satellite imagery that monitors farm conditions. Companies like Apollo Agriculture and iProcure have collectively served over 150,000 farmers with these technologies.
Can I really learn AI without a technical background?
Yes, you can start learning AI without a technical background. Many resources like Elements of AI and Kenya.ai’s Beginner Track are designed for non-technical learners. These focus on understanding AI concepts, applications, and implications rather than technical implementation. You can gradually build technical skills as needed.
Is the Kenyan government using AI to monitor citizens?
The Kenyan government is using AI in limited ways for service delivery and security, such as traffic monitoring and immigration processing. However, there are concerns about privacy and surveillance. The Data Protection Act (2019) provides some safeguards, and the National AI Strategy includes provisions for ethical AI governance and protecting citizens’ rights.
Will AI take away jobs in Kenya?
AI will likely transform rather than eliminate jobs in Kenya. While some routine tasks may be automated, new roles will emerge in AI development, ethics, data annotation, and system maintenance. The government estimates AI could create over 100,000 new jobs by 2030, though workers will need to adapt and acquire new skills.
How much does it cost to implement AI in a Kenyan business?
The cost varies widely depending on the application. Simple AI tools like chatbots or basic analytics can cost as little as KES 50,000-100,000 to implement. More complex custom solutions can range from KES 500,000 to several million shillings. Many businesses start with small pilot projects to demonstrate value before larger investments.
What languages do AI systems in Kenya support?
Most AI systems in Kenya support English, with growing support for Swahili. Some platforms like Safaricom’s Zuri chatbot can communicate in both languages. There’s ongoing work to expand support for other local languages, though this remains limited due to the data requirements for training language models.
How can I protect my data when using AI services in Kenya?
To protect your data when using AI services in Kenya, understand what data is being collected and how it will be used, only provide necessary information, use services with clear privacy policies, report concerns to the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner, and exercise your rights under the Data Protection Act (2019) to access or delete your data.
Conclusion: Joining Kenya’s AI Journey
Artificial Intelligence represents both tremendous opportunity and significant responsibility for Kenya. As this technology transforms sectors from agriculture to finance, Kenya has the chance to leapfrog traditional development hurdles and position itself as Africa’s AI leader.
Whether you’re a student looking to build future-proof skills, a business owner seeking efficiency gains, a policymaker shaping the regulatory environment, or simply a curious citizen, now is the time to engage with AI. The technology is no longer coming, it’s here, and it’s already changing how Kenyans live, work, and solve problems.
By understanding AI’s potential and pitfalls, participating in the growing AI community, and advocating for responsible development, we can all help shape an AI powered future that works for all Kenyans.